Weekly Tech+Bio Highlights #18
ALSO: Kidney-On-Chip in Space; New Foundation Model for Small Molecule Discovery; Adaptive Oncology Trials...
Hi! This is our weekly newsletter, ‘Where Tech Meets Bio,’ where we talk about technologies, breakthroughs, and great companies moving the biopharma and medtech industries forward.
If you've received it, then you either subscribed or someone forwarded it to you. If that is the case, subscribe by clicking this button:
We’re pleased to announce our invitation as a media outlet to the Financial Times Live Global Pharma and Biotech Summit on November 5-7, 2024.
We’re excited to have our CEO, Tanya Bell, attending and representing us. The summit boasts an impressive lineup of speakers, including Amanda Pritchard, Chief Executive of NHS England, and Demis Hassabis, 2024 Nobel Prize winner, among others.
If you’re attending and would like to connect, don’t hesitate to reach out—we’d love to discuss new ideas and potential collaborations!
Now, let’s get to this week’s topics.
Brief Insights
📈 Global pharmaceutical R&D spending has reached an estimated $276 billion annually, significantly higher than previous figures, according to a comprehensive study in Nature Reviews Drug Discovery.
🔬 A 31-year study by the Wellcome Sanger Institute and University of Zurich reveals how stem cell transplants from younger donors lead to stronger, long-term immune system resilience in recipients, while transplants from older donors result in fewer surviving stem cells, affecting transplant success and immune recovery.
🔬 Iambic Therapeutics launches Enchant AI, a multi-modal transformer model that predicts clinical outcomes using preclinical data, aiming to reduce drug development timelines and costs by bridging the preclinical-clinical data gap and achieving superior accuracy in pharmacokinetics predictions.
🔬 Insilico Medicine, in collaboration with Sanofi, reports an advancement in AI-driven oncology drug discovery, developing a lead molecule targeting an "undruggable" transcription factor site using Insilico's PandaOmics and Chemistry42 platforms, with potential milestone payments up to $1.2 billion.
💰 Ataraxis AI launches with $4M in seed funding to develop AI-driven cancer diagnostics, starting with Ataraxis Breast, a tool offering up to 30% improved accuracy in breast cancer risk assessment to potentially reduce unnecessary chemotherapy for thousands of patients annually.
🔬 Lexeo Therapeutics' LX1001 gene therapy shows promising Phase 1/2 trial results for APOE4-associated Alzheimer’s, demonstrating dose-dependent increases in APOE2 expression, reductions in tau biomarkers, and a favorable safety profile, particularly benefiting patients with moderate Alzheimer’s.
💰 Archon Biosciences secures $20M in seed funding to develop "antibody cages", an AI-enhanced technology that adds tailored protein structures to antibodies, aiming to expand therapeutic capabilities and improve antibody targeting for conditions lacking approved treatments.
🔬 Medable launches its Digital and Decentralized Clinical Trial Platform on Google Cloud Marketplace, enhancing trial design and management with AI and data integration to accelerate trial efficiency, patient enrollment, and accessibility in a globally compliant, cloud-based environment.
💰 Quris-AI acquires Nortis to integrate its Kidney-on-Chip technology that seen employment in space into Quris's Bio-AI platform. More on that in the feature section.
🔬 The Novo Nordisk Foundation launches Gefion, Denmark’s first AI supercomputer, with $87 million in funding, to accelerate drug discovery, quantum computing, and climate research.
🔬 Absci and Twist Bioscience team up to design a novel therapeutic antibody, combining Absci’s generative AI drug design with Twist’s high-fidelity DNA synthesis to accelerate antibody development and streamline the transition from AI-driven design to physical testing.
🔬 Evogene partners with Google Cloud to develop an AI foundation model for small molecule discovery, using Google’s Vertex AI and Compute Engine to accelerate drug and crop protection innovation, with applications across pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and environmental sustainability.
💰 Accenture Ventures invests in 1910 Genetics to integrate AI into drug discovery, combining Accenture’s AI expertise with 1910’s multimodal platform to streamline molecule design and target identification, aiming to reduce R&D costs and enhance therapeutic accessibility across biopharma.
🔬 Okomera secures a €1.5M Bpifrance grant to advance an AI and microfluidics-powered CRISPR platform for cancer target validation, partnering with Marseille's Paoli-Calmettes Institute to enhance drug discovery using patient-derived organoids.
💰 Benchling has acquired bioinformatics company PipeBio to enhance its AI-powered antibody discovery platform, combining Benchling’s R&D management tools with PipeBio’s large-scale sequence analysis capabilities, enabling researchers to screen millions of sequences and streamline biologics discovery and development.
🔬 Laverock Therapeutics showcased its latest findings on the GEiGS gene-silencing platform at ESGCT 2024, highlighting its ability to silence multiple genes simultaneously and its tenfold increase in screening capacity, now evaluating 6,000 RNA designs per target, enabling rapid advancements in oncology applications like CAR T cells and tumor-responsive macrophages.
🔬 Life Biosciences presented new data at AAO 2024 on its epigenetic reprogramming gene therapy, ER-100, demonstrating improved retinal ganglion cell function and restored visual function in a nonhuman primate model of optic neuropathy, replicating earlier findings and confirming dosing strategies.
Human trials are expected in 2025.
🔬 Recursion has begun a Phase 2 trial for REC-3964, a non-antibiotic, AI-developed small molecule targeting recurrent C. difficile infections, aiming to spare healthy gut bacteria and reduce infection recurrence rates.
Kidney-On-Chip in Space: Quris Acquires Nortis
Quris-AI recently acquired Nortis, a developer of Kidney-on-Chip technology that has been used in the NIH’s “Tissue Chips in Space” initiative led by NCATS in collaboration with NASA and the ISS National Lab.
In the program, launched in 2017, the idea is to study organ functions—including kidney function—under the unique conditions of microgravity. By 2021, kidney tissue chips had already completed two flights to the ISS. Providing a close-up on how kidneys respond to toxic or pharmacokinetic challenges in an accelerated, high-stress environment, these chips let us observe drug impacts that might not show up until later stages in typical preclinical tests.
Now, with Quris-AI’s Bio-AI platform onboard, Nortis’s system gets an AI boost aimed at enhancing drug safety predictions for kidney toxicity. The system uses human-derived kidney tissue to replicate core functions like filtration and electrolyte balance, getting closer to the complexity of human responses than animal models typically can. Research has shown this to be valuable: Nortis’s triple single-channel (TSC) chip, for example, was used to evaluate nephrotoxic effects of drug candidates, detecting injury markers that weren’t apparent in animal tests.
Evogene and Google Cloud Collaborate on Foundation Model for Small Molecule Discovery
Evogene Ltd., a computational biology firm, has partnered with Google Cloud to develop an advanced AI foundation model for small molecule discovery. This new model will be built upon Evogene's existing ChemPass AI platform, which is integrated with Google Cloud’s Vertex AI and Compute Engine infrastructure.
The partnership aims to develop a foundation model trained on 40 billion molecular structures, leveraging Google Cloud’s GPU power
Founded in 2002, Evogene Ltd. initially concentrated on agriculture, focusing on seed traits, biological stimulants, and agrochemicals. However, by 2017, the company began expanding into health-focused fields, launching Biomica, its subsidiary for microbiome-based therapeutics, to explore pharmaceutical applications. Since agriculture is outside our usual scope, let’s briefly look at Biomica.
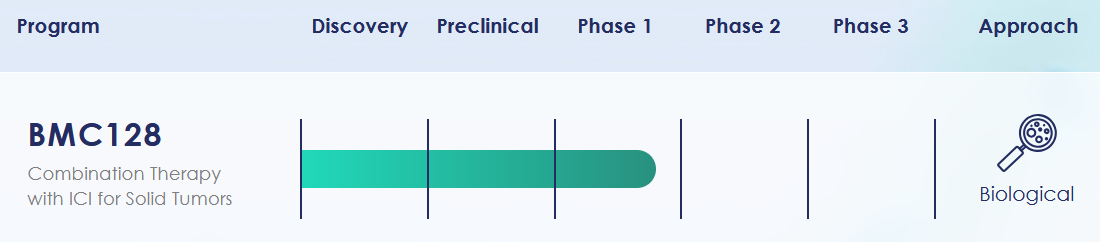
In 2023, Biomica completed a $20 million financing round to support their ongoing BMC128 Phase 1 immuno-oncology trial, and scale GMP production of its IBD candidate BMC333 for a Phase 1 trial.
Biomica’s pipeline includes microbiome-based therapies for immuno-oncology, gastrointestinal disorders, and antimicrobial resistance (developed with Nobel laureate Prof. Ada Yonath). The one ahead is BMC128, now in Phase 1 trials. Combined with Bristol Myers Squibb’s Opdivo, early data indicates a strong safety profile and a 72% response rate in patients previously resistant to treatment.
Returning to the broader perspective, Evogene’s main technology, the Computational Predictive Biology (CPB) platform, integrates biological insights with big data and AI to facilitate the discovery and optimization of life science products, such as small molecules, microbes, and genetic elements.
The CPB platform uses what they call a "connecting the dots" approach, rejecting the slow, linear discovery model. By processing biological, chemical, and genetic data in parallel, the approach is intented to accelerate candidate selection, reduce trial-and-error, and avoid bottlenecks from sequential stages.
Their computational biology relies on a collection of specialized AI-driven tools, each tailored to different aspects product development. Let’s have a look:
MicroBoost AI—enhances discovery and development of microbial products for health, agriculture, and industry. Identifies microbial candidates and the genes underlying their functions, supporting development through microbial consortia design, formulation, and variant analysis (e.g. Biomica’s BMC128, a microbiome-based therapeutic designed to enhance cancer immunotherapy).
ChemPass AI—is focused on small molecule product discovery and optimization. Uses chemo-informatics and deep learning to screen over 35 billion molecules, selecting candidates with desired attributes (e.g., ADME-Tox properties) and optimizing them via structure-activity relationship analysis.
GeneRator AI—aids in discovering and developing products based on genetic elements. Identifies and selects gene candidates linked to specific phenotypes, enabling genetic engineering applications. Development tools include phylogenetic and pathway analysis to refine genetic hits.
Through the partnership with Google Cloud, Evogene’s foundation model will scale up these capabilities.
Winners of the Evolved 2024 Hackathon
We’re excited to share a few highlights from the Evolved 2024 Hackathon—a week packed with ambitious projects and talent in computational biology and AI. Hosted by EvolutionaryScale and Enveda Bio, this hackathon brought in partners like OpenAI, AWS, DigitalOcean, and Polaris to provide everything from compute power to wet-lab validation and prize incentives.
Nearly 860 interested competitors joined the hackathon from around the world—including Japan, India, Germany, and Chile. From this pool, 82 teams (537 participants) officially applied, with 20 standout teams selected to compete. These teams brought a diverse mix of academic researchers from top labs (such as Stanford and UToronto), early-stage bio startup founders, and ML engineers from prominent tech and biotech companies, including Microsoft, Ginkgo, and BigHat Bio.
A lineup of 21 judges—from DARPA, NVIDIA, AWS, and top computational bio platforms—evaluated the projects, awarding prizes to 8 teams that tackled challenges in protein modeling, gene delivery, and molecular spectra prediction. The winning teams received tech credits to access the world’s leading computational infrastructure, cash prizes, and exclusive business development and fundraising opportunities:
EvoCapsid
Custom gene delivery agents via ML workflow for cargo selection and targeted deliveryMSEffect
MS/MS predictions for identifying unknown molecular spectraGenPlasmid
Automated plasmid design to streamline molecular biology workflowsInterprotability
Interpreting protein language model features to reveal biological functionsSilica
Computational pipelines to optimize enzyme and nanobody stability and bindingMorphoLogic AI
AI-driven analysis of cellular morphology to understand disease effects and drug responsesGLIMPSE (Graph-Language AI for Multi-Query Prediction and Scientific Exploration)
Cellular morphology analysis using AI for disease, drug, and transcriptional changesBST
Midbrain organoid platform for Parkinson’s disease, combined with foundation model-based network analysis
We're looking forward to featuring EvoCapsid, this year’s top team. More on their approach and vision in the next issue.
MEDSIR’s Adaptive Oncology Trials and Precision Medicine
We recently explored MEDSIR’s (Medica Scientia Innovation Research) work in oncology clinical trials, spotlighting their focus on adaptive design and precision medicine to transform patient outcomes.
Our interview with Rui Rui Zhang Xiang delves into MEDSIR’s unique approach to clinical trials, particularly through studies like the PHERGain trial, which examines chemotherapy-free treatment options for HER2-positive breast cancer, aimed at enhancing patients' quality of life.
Key discussion points include the use of adaptive trial designs that adjust based on real-time data, precision medicine approaches driven by biomarkers for tailored treatment, and AI-integrated tools alongside real-world evidence to refine patient selection and trial efficiency. Patient-centric strategies—such as collaboration with advocacy groups—enhance engagement and retention, while flexible regulatory approaches enable effective multicenter trials, advancing oncology research towards a more personalized and responsive framework.
For more on transformative strategies in oncology—read the full interview.
Read also:
14 Foundation Models for Biology Research and Chemistry