Weekly Tech+Bio Highlights #3
ALSO: AI Foundation Models for Digital Pathology and Mass Spectrometry; Booming Radiopharmaceuticals and Shortage of Ac-225; The Rise of Cyclic Peptides: Bridging the Gap in Modern Medicine
Hi! I am Andrii Buvailo, and this is my weekly newsletter, ‘Where Tech Meets Bio,’ where I talk about technologies, breakthroughs, and great companies moving the biopharma industry forward.
If you've received it, then you either subscribed or someone forwarded it to you. If the latter is the case, subscribe by pressing this button:
Now, let’s get to this week’s topics!
News Highlights
🚀 Cradle, co-founded by Laura Deming and Hunter C Davis, secured $48 million to develop reversible cryonics technology. The startup aims to achieve whole-body cryopreservation by pausing and restarting biological functions, demonstrated by their recovery of electrical activity in cryopreserved neural tissue, with future goals including preserving whole organs and conducting human clinical trials.
🔬 Structure Therapeutics' stock rose 33% this year due to promising phase 2a clinical trial data for its obesity drug, GSBR-1290, which shows faster weight loss compared to Novo Nordisk’s Wegovy and Eli Lilly's Zepbound.
💰 ITM Isotope Technologies Munich (ITM) secured a $204.6M investment, led by Temasek with contributions from BlackRock, Qatar Investment Authority, ATHOS, and Carbyne, to advance its radiopharmaceutical pipeline and support the commercial launch of its Phase III lead candidate, ITM-11, for treating gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.
📈 Tempus AI, a precision medicine company, announces terms for its $400 million IPO, offering 11.1 million shares at $35-$37 each, aiming for a $6.2 billion market value. The Chicago-based firm, with $562 million in recent revenue, plans to list on Nasdaq under "TEM" the week of June 10, 2024.
🔬 Merck KGaA partners with Biolojic Design in a $376M deal to develop AI-designed antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) targeting oncology and immunology. This collaboration aims to create multispecific antibodies that enhance tumor targeting while minimizing damage to healthy tissues, leveraging Biolojic's platform known for the first AI-designed antibody in clinical trials.
🔬 AAV-based gene therapy restored hearing in both ears of children with hereditary deafness caused by OTOF gene mutations, significantly improving sound localization and speech perception, in a groundbreaking clinical trial in Shanghai led by Mass Eye and Ear and Fudan University.
🔬 Moderna and Merck's combined melanoma therapy with Keytruda shows a significant survival rate improvement, with nearly 75% of patients cancer-free at 2½ years compared to 55.6% with Keytruda alone, highlighting the potential of their mRNA vaccine.
🔬 Clinical trials for the world's first tooth regrowth medicine will begin in September 2024 at Kyoto University Hospital. Led by Kitano Hospital's Katsu Takahashi, the trials aim to treat patients with congenital tooth deficiency by deactivating the USAG-1 protein, potentially enabling tooth growth in those missing teeth due to genetic conditions, cavities, or injuries.
🚀 Weave Bio secures $10M in seed funding to launch AutoIND, an AI-powered platform that automates and accelerates the drafting, reviewing, and submitting of regulatory documents in drug development, reducing submission times by over 50%.
🏭 Thermo Fisher Scientific opens a new GMP-certified ultra-cold facility in Bleiswijk, Netherlands, to accelerate advanced therapies development, offering comprehensive clinical trial support for cell and gene therapies, biologics, antibodies, and vaccines.
🔬 Paige launches new service line with advanced multi-modal AI models, including the updated Virchow and new PRISM Foundation Model, to enhance precision oncology, cancer diagnosis, and drug discovery.
💰 Ipsen and Marengo Therapeutics expand their deal to develop two trispecific antibody assets targeting cold tumors, potentially worth up to $1.2 billion, aiming to enhance T cell quality and therapy durability by targeting T cell receptors Vβ6 and Vβ10, moving beyond the conventional CD3-targeting T cell engagers.
📈 Rapport Therapeutics, backed by Johnson & Johnson, lists on Nasdaq under the ticker "RAPP," pricing its IPO at $17 per share, with 8 million shares offered, potentially raising $154 million, including a concurrent private placement. It plans to develop a tablet and long-acting injectable for epilepsy, with a Phase 2a trial for adults starting soon.
🏭 Molecular Devices inaugurates a state-of-the-art facility in Cardiff, Wales, for large-scale production of patient-derived organoids, enhancing drug discovery and precision medicine capabilities. Nobel Laureate Professor Sir Martin Evans celebrated the opening, emphasizing its impact on pharmaceutical research.
🏭 WACKER opens a €100 million mRNA competence center in Halle, Germany, tripling production capacity for mRNA-based active ingredients, including anti-COVID vaccines. Partnering with CordenPharma, WACKER will produce 80 million mRNA vaccine doses annually for future pandemics under a German government contract with a five-year stand-by phase.
💡 Envisagenics, an AI-enabled biotech specializing in RNA splicing therapeutics, raised $25 million in its Series B funding round with investments from Bristol Myers Squibb and other supporters, to advance its preclinical oncology pipeline using its AI drug discovery platform, SpliceCore.
💰 GSK acquires San Diego-based RNA startup Elsie Biotechnologies, enhancing its nucleic acid drug pipeline, including hepatitis B candidate bepirovirsen, and advancing oligonucleotide drug development.
🚀 Alphabet Inc. announced the appointment of Anat Ashkenazi as its new CFO, offering her a $9.9 million signing bonus, $13.1 million in stock options, and a $1 million annual salary. Ashkenazi, a former Eli Lilly executive, will transition to Google at the end of July.
🔬 23andMe announces positive preliminary Phase 2 results for 23ME-00610, demonstrating clinical benefit and safety in neuroendocrine and ovarian cancer patients, with tumor CD200 identified as a potential efficacy biomarker.
A Multi-Modal Generative Foundation Model for Slide-Level Histopathology
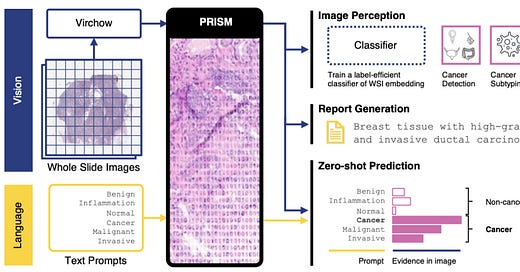
Paige, a provider of digital pathology solutions and AI applications, has launched a new service line leveraging its Foundation Models. These models include a large multi-modal AI model in pathology and oncology. The new service is intended to assist AI developers, computational pathology product creators, and life sciences companies in developing AI models for applications such as research and development, clinical trials, and commercial needs. The initiative aims to contribute to advancements in precision oncology, with the goal of improving cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Paige’s Foundation Models offer a distinct approach compared to traditional AI development methods. Conventional methods often require specific models to be trained for individual tasks using specific data, a process that is both time-consuming and resource-intensive. Paige’s models, however, can be adapted to a wide range of tasks without the need for individual training on each task. This flexibility has the potential to reduce the time and computational resources needed and lower the data requirements for developing advanced AI systems.
The new service line provides access to advanced pre-trained models, including updated versions of Virchow, described as the largest image-based AI model aimed at addressing cancer, and the newly released PRISM Foundation Model. PRISM, a multi-modal slide-level model, is designed to enhance reporting and generative capabilities, offering analytical data for multi-tissue and rare cancer detection, rare biomarker identification, cellular subtyping, spatial biology, and therapy response prediction. This specificity and accuracy were, reportedly, not previously accessible with older technologies.
The Largest AI Foundation Model for Mass Spectra Analysis
Enveda Biosciences, a techbio company headquartered in Boulder, Colorado, has unveiled PRISM (Pretrained Representations Informed by Spectral Masking), a foundation model trained on 1.2 billion small molecule mass spectra. This development aims to enhance the identification and prediction of molecular structures, supporting advancements in drug discovery.
In the field of natural products, 99.9% of small molecules remain unknown to science. These molecules, found in complex mixtures, are challenging to identify using traditional methods that require isolation and purification. Mass spectrometry (MS) offers an alternative by acquiring identifying information on numerous new molecules simultaneously. However, interpreting mass spectra has been limited by the small number of annotated reference spectra available.
PRISM addresses this challenge by using self-supervised learning on a large dataset of unannotated spectra. Similar to models in natural language processing like GPT and BERT, PRISM improves the prediction of molecular identities through advanced machine learning techniques and a comprehensive training set.
Key Takeaways
Training Scale: PRISM is trained on 1.2 billion small molecule mass spectra, the largest dataset assembled for this purpose, including both public repositories and Enveda’s proprietary data.
Self-Supervised Learning: The model employs a masked peak modeling approach, analogous to masked language modeling in NLP, enabling it to predict missing mass peaks and learn the grammar of mass spectra.
Predictive Power: PRISM improves the prediction of chemical properties and the matching of unknown spectra to reference libraries, with a 23% improvement in spectral matching tasks.
Drug Discovery: By better interpreting mass spectra, PRISM aids drug hunters in identifying potential new medicines from the vast reservoir of natural molecules.
Future Expansion: Enveda plans to expand the PRISM dataset, enhancing the model’s predictive capabilities and further supporting the discovery of novel therapeutics.
Radiopharmaceutical Company Targets $202M IPO in the US
Amidst the growing interest in radiopharmaceuticals, Telix Pharmaceuticals, estimates that the net proceeds from the offering will be $183 million, potentially rising to $211 million if underwriters fully exercise their option to purchase additional shares.
As reported by Lei Lei Wu, Australian biotech Telix Pharmaceuticals, which is already listed on the Australian Stock Exchange, intends to list on Nasdaq under the ticker symbol $TLX.
Telix has two approved radioisotope diagnostics and is awaiting an FDA decision on two more. Additionally, the company is developing a range of experimental radiotherapies, including treatments for prostate cancer, kidney cancer, and glioblastoma, an aggressive brain cancer.
Its leading prostate cancer drug candidate is in a Phase 3 trial, with interim data expected in the first half of 2025.
Radio-imaging using targeted radiation relies heavily on digital data processing and input from highly trained technicians and radiologists to correctly interpret data.
Telix uses AI technology to transform image analysis by improving the accuracy and speed of decision-making for clinicians by recognising complex patterns in large datasets and conducting predictive analysis.
While Booming, Radiopharmaceuticals Companies Grapple With Isotope Supply
As was reported by Endpoints News, RayzeBio, a biopharmaceutical company, is facing supply challenges with actinium isotopes needed for its international studies. Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), which announced plans to acquire RayzeBio for $4.1 billion, has had to pause a critical Phase 3 trial due to this isotope shortage. This pause highlights broader supply chain issues in the radiopharmaceutical sector, which is seeing increased demand and investment.
Key Takeaways:
Supply Dependency: RayzeBio has been arguably dependent on a Russian supplier for actinium-225 (Ac225) isotopes used in international clinical studies, with the U.S. Department of Energy providing supplies only for domestic use.
Manufacturing Plans: BMS is setting up a GMP manufacturing facility in Indiana to produce Ac225 by Q1 2025, aiming to reduce reliance on third-party suppliers and secure a stable isotope supply for future trials.
Industry Challenges: The radiopharmaceutical sector faces significant supply chain difficulties, with limited global suppliers for Ac225. This has led to heightened demand and competition for securing isotope supplies.
Future Outlook: More companies are planning to enter the actinium supply market, with NorthStar Medical Radioisotopes expected to begin supplying by 2025. The situation is seen as a misalignment of supply and demand rather than an outright shortage, reflecting the growing pains of a rapidly expanding field.
The Rise of Cyclic Peptides: Bridging the Gap in Modern Medicine
Cyclic peptides, characterized by their unique ring structures, represent an emerging trend in drug discovery due to their ability to bridge the gap between small molecules and biologics.
These "Goldilocks" molecules are not too large like monoclonal antibodies, which require injection, nor too small like traditional oral drugs, which often struggle with complex protein-protein interactions.
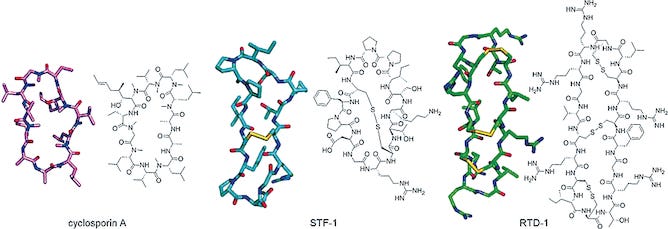
For instance, Merck's research highlights the potential of macrocyclic peptides to cover extensive surface areas, making them highly effective in disrupting protein interactions crucial to various diseases.
Protagonist Therapeutics' recent success with JNJ-2113, the first oral IL-23 receptor antagonist, underscores the therapeutic promise of cyclic peptides in treating conditions like moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis.
The positive results from the Phase 2b FRONTIER 1 trial indicate not only efficacy but also tolerability, paving the way for further development in other immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.
These advancements reflect the growing importance of cyclic peptides in expanding the therapeutic landscape, offering new avenues for oral treatments previously dominated by injectable biologics. As research and development in this field progresses, cyclic peptides are poised to significantly enhance the range and accessibility of treatments for complex diseases.
There are a number of drug discovery startups developing second generation cyclic peptides of second generation, including modified peptides and peptidomimetics. Below we summarized 5 such companies.