Weekly Tech+Bio Highlights #36: Defining Modern AI Drug Discovery
Also: Neuroscientists Map Cubic Millimeter of Mouse Brain, Moving Away from Animal Testing & Industry Highlights
Hi! This is BiopharmaTrend’s weekly newsletter, Where Tech Meets Bio, where we explore technologies, breakthroughs, and cutting-edge companies.
We’ve also just released a new report outlining a framework for what defines modern AI-driven drug discovery, for 2025 and beyond.
If this newsletter is in your inbox, it’s because you subscribed or someone thought you might enjoy it. In either case, you can subscribe directly by clicking this button:
Let’s get to this week’s topics!
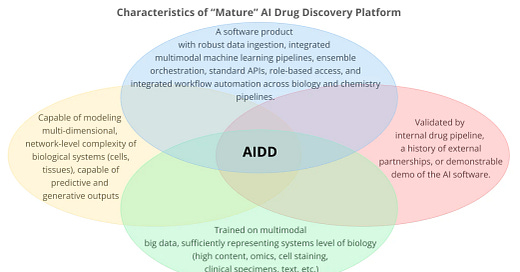
Defining Modern AI Drug Discovery
The definition of “AI Drug Discovery” is evolving. In
's new report, we set a clear framework for identifying technologies beyond legacy computational tools.This year's analysis introduces a qualitative framework highlighting four essential pillars distinguishing genuine AI-driven drug discovery companies:
Holism over reductionism: Moving beyond narrow biological targets, using multimodal data (phenotypes, omics, patient records) to create comprehensive biological models.
Scalable software infrastructure: Not just standalone algorithms, but robust software platforms that seamlessly fit into real-world R&D workflows, capable of consistently delivering repeatable outcomes.
Deep data integration: Prioritizing acquisition and practical use of extensive multimodal datasets like those from advanced proteomics, NGS, clinical records, or robotic lab experiments.
Proven validation: Clear demonstrations of success through internal pipelines, third-party collaborations, scientific publications, patents, and actual progress in clinical development.
Modern AI-driven drug discovery represents a conceptual shift from traditional cheminformatics and bioinformatics methods, moving toward systems-level biology modeling powered by generative AI architectures and transformer-based models.
The report focuses on technical and methodological considerations, with select examples drawn from companies such as BenevolentAI, Healx, Insilico Medicine, Schrodinger, Relay Therapeutics, Recursion, Valo Health, Verge Genomics, and others to illustrate different approaches to pipeline design, model validation, and software infrastructure.
🤖 AI x Bio
(AI applications in drug discovery, biotech, and healthcare)
🔹 The FDA has announced plans to phase out animal testing in drug evaluation, starting with monoclonal antibodies, in favor of AI models, organoids, and organ-on-chip systems.
🔹 The Institute for Protein Design and MIT have released RFdiffusion2, an AI model that builds enzymes from chemical reactions instead of protein templates. It solved all 41 benchmark tasks and generated active enzymes for five reactions. Model and data will be open source.
🔹 AI-native biotech Noetik has appointed Dr. Emily Corse, a cancer immunotherapy expert, as EVP of Therapeutics to lead its cancer drug pipeline.
🔹 GenomOncology’s CTO Ian Maurer has announced BioMCP, an open-source protocol server that equips AI assistants with real-time context from PubMed, ClinicalTrials.gov, and genomic variant databases to support biomedical research.
🔹 AI-driven clinical trial company Unlearn has named Krates Ng as CTO to scale its digital twin tech. Ng brings nearly 30 years of engineering leadership and will focus on expanding Unlearn’s AI solutions for drug development.
🔹 IQVIA has launched a compact medical LLM that reportedly outperforms larger models like GPT-4 on clinical reasoning tasks, offering step-by-step transparency and practical deployment for healthcare and life sciences workflows.
🔹 Recursion has dosed the first patient in a Phase 1 trial of REC-3565, an AI-designed MALT1 inhibitor for B-cell lymphomas, developed in 15 months using its Recursion OS drug discovery platform.
🔹 Enamine and Recursion have released AI-curated screening libraries targeting 100 hard-to-drug biological targets, combining Recursion’s machine learning with Enamine’s 65B-compound REAL Space to streamline early-stage hit discovery with focused, synthesizable compound sets.
🔹 Biostate AI has partnered with the Accelerated Cure Project to develop transformer-based predictive models for multiple sclerosis, using RNAseq data from one of the world’s largest MS biorepositories to forecast disease progression and treatment response.
🔹 Verge Genomics has reported that digital biomarkers—captured via sensors, wearables, and speech platforms—may track early ALS progression before treatment, suggesting a new way to measure efficacy in neuro trials during pre-treatment phases.
🔹 Pharma logistics: SkyCell has partnered with Microsoft to launch an AI co-pilot built on Azure OpenAI to monitor cold-chain shipments in real time, aiming to reduce drug losses and streamline supply chain decisions directly within Microsoft Teams.
🔹 Enterprise automation firm UiPath has partnered with Google Cloud to launch a generative AI medical summarization agent, aiming to reduce prior authorization turnaround times by up to 50% and streamline healthcare workflows using Google’s Vertex AI and Gemini models.
🔹 Healthtech company Flatiron Health has partnered with AI-driven trial recruitment firm Massive Bio to improve patient identification and enrollment in cancer clinical trials across the U.S., aiming to accelerate access to studies by linking eligible patients to nearby research sites.
🔹 AI health screening company Predictmedix AI has surpassed 500,000 scans with its Smart Health AI Stations, using non-invasive, machine learning-powered tools to enable real-time detection of physical and mental health risks across healthcare, corporate, and public settings.
🔹 Genomics company Valted Seq has launched an AI-powered tool trained on tens of millions of in-house single cells, to enable more accurate and scalable analysis of complex single-cell genomics data, reportedly outperforming general AI models in tasks critical to biomarker discovery and precision medicine.
🔹 Worldwide Clinical Trials, a global CRO focused on neuroscience, oncology, rare and cardiometabolic diseases, has added an AI-driven capability to optimize clinical trials by identifying patients most likely to respond to treatment.
🚜 Market Movers
(News from established pharma and tech giants)
🔹 Novartis has announced a $23B investment to expand U.S. manufacturing and R&D across 10 sites, joining Eli Lilly and Johnson & Johnson in ramping up domestic production amid tariff threats and a shifting trade landscape, as pharma firms race to localize operations and safeguard supply chains.
🔹 DHL Group, a global logistics and supply chain leader, has announced a €2B investment through 2030 to expand its healthcare logistics division.
💰 Money Flows
(Funding rounds, IPOs, and M&A for startups and smaller companies)
🔹 Warsaw-based Ingenix.ai has raised €9M to develop a multimodal AI foundation model that simulates clinical trials using digital twins.
🔹 Neuranics, a deep-tech spinout from the Universities of Glasgow and Edinburgh, has raised $8M to advance its ultra-sensitive TMR magnetic sensing tech, aiming to enable contactless muscle and heart signal tracking for next-gen XR, wearables, and human-machine interfaces.
🔹 BayPine has acquired clinical trial site network CenExel, which specializes in CNS disorders, with plans to expand its digital infrastructure and apply AI to boost trial execution and site performance across its 18 U.S. locations.
🔹 Newcastle-based Aelius Biotech has raised £750K to expand its in vitro gut model platform, which simulates full intestinal absorption without animal testing, supporting drug and food R&D for clients like Huel and cultivated meat startups.
🔹 Data valuation and collateralization firm Gulp Data has estimated 23andMe’s genetic and health data at $289M amid the company’s bankruptcy filing.
🔹 OS Therapies, a clinical-stage cancer immunotherapy company, has acquired Advaxis’s listeria-based immunotherapy assets from Ayala Pharmaceuticals, while also advancing next-gen “tunable” ADC and drug conjugate programs targeting solid tumors.
🔹 Immunotherapy company ImmunityBio has raised $75M in equity financing to support operations and expand access to its FDA-approved bladder cancer therapy, with new FDA submissions for expanded indications.
🔹 Merida Biosciences has launched with $121M in Series A funding to develop precision antibody-depleting therapies for autoimmune and allergic diseases, aiming to eliminate disease-driving antibodies without broad immunosuppression.
🔹 Immunology-focused RayThera has raised $110M in Series A to advance its small molecule drug candidates into Phase 1 trials.
⚙️ Other Tech
(Innovations across quantum computing, BCIs, gene editing, and more)
🔹 A $200 blood test measuring p-Tau217 can reportedly detect Alzheimer’s disease up to 20 years before symptoms appear, rivaling PET scans in accuracy and opening the door for early lifestyle or drug interventions to delay or prevent disease onset.
🔹 De-extinction company Colossal Biosciences has produced the first genetically engineered animals with dire wolf-like traits, using multipoint genome editing in gray wolf cells to recreate key features of the extinct species, marking a milestone in synthetic biology.
🔹 CytoTronics has introduced a neural screening tool that captures structure and activity from the same neurons at scale to enable faster drug discovery for neurological diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and ALS across thousands of wells simultaneously.
🔹 EHR data company OMNY Health has become the first to offer its dataset on Datavant Connect via AWS Clean Rooms to enable faster, more efficient access to real-world clinical data for research and drug development.
🔹 Womed has launched its fertility-preserving device in 14 European countries, marking the first distribution of a film-based barrier designed to prevent intrauterine adhesions—a major cause of infertility—following uterine procedures.
🔹 Fertility-focused biotech Gameto has reported a 44% pregnancy rate per cycle using its iPSC-derived Fertilo platform, more than doubling standard IVM outcomes, to enable safer, faster, and less invasive egg maturation with lab-grown ovarian support cells.
🔹 Molecular diagnostics company Alveo Technologies, which develops rapid pathogen detection tools, has appointed Nobel Laureate Dr. James Rothman—recognized for his work on cellular transport systems—to its board to help scale its infectious disease testing platform.
🏛️ Bioeconomy & Society
(News on centers, regulatory updates, and broader biotech ecosystem developments)
🔹 Scotland has launched the ‘AI Discovery’ programme to turn academic research into NHS healthcare innovations, training postgraduates to build AI-driven startups through a government-backed initiative led by CodeBase and major universities.
🔹 With IPOs and M&A largely off the table, biotechs are turning to cash-preserving strategies to survive a volatile market, according to Endpoints News, which outlines a survival playbook featuring insights from industry veteran John Maraganore.
🔹 The National Security Commission on Emerging Biotechnology has called for a $15B investment in the sector, urging U.S. action to stay competitive with China as lawmakers and experts highlight biotech as a critical arena for national security and innovation.
Neuroscientists Map Cubic Millimeter of Mouse Brain
In a landmark achievement (detailed in New York Times) for large-scale connectomics, a team of over 100 researchers has mapped the structural and functional wiring of a cubic millimeter of mouse brain—capturing 200,000 cells and 523 million synapses. The MICrONS project, led by the Allen Institute, Princeton University, and Baylor College of Medicine, paired in vivo activity recording with high-resolution 3D reconstructions generated from 28,000 brain slices and 1.6 petabytes of imaging data.
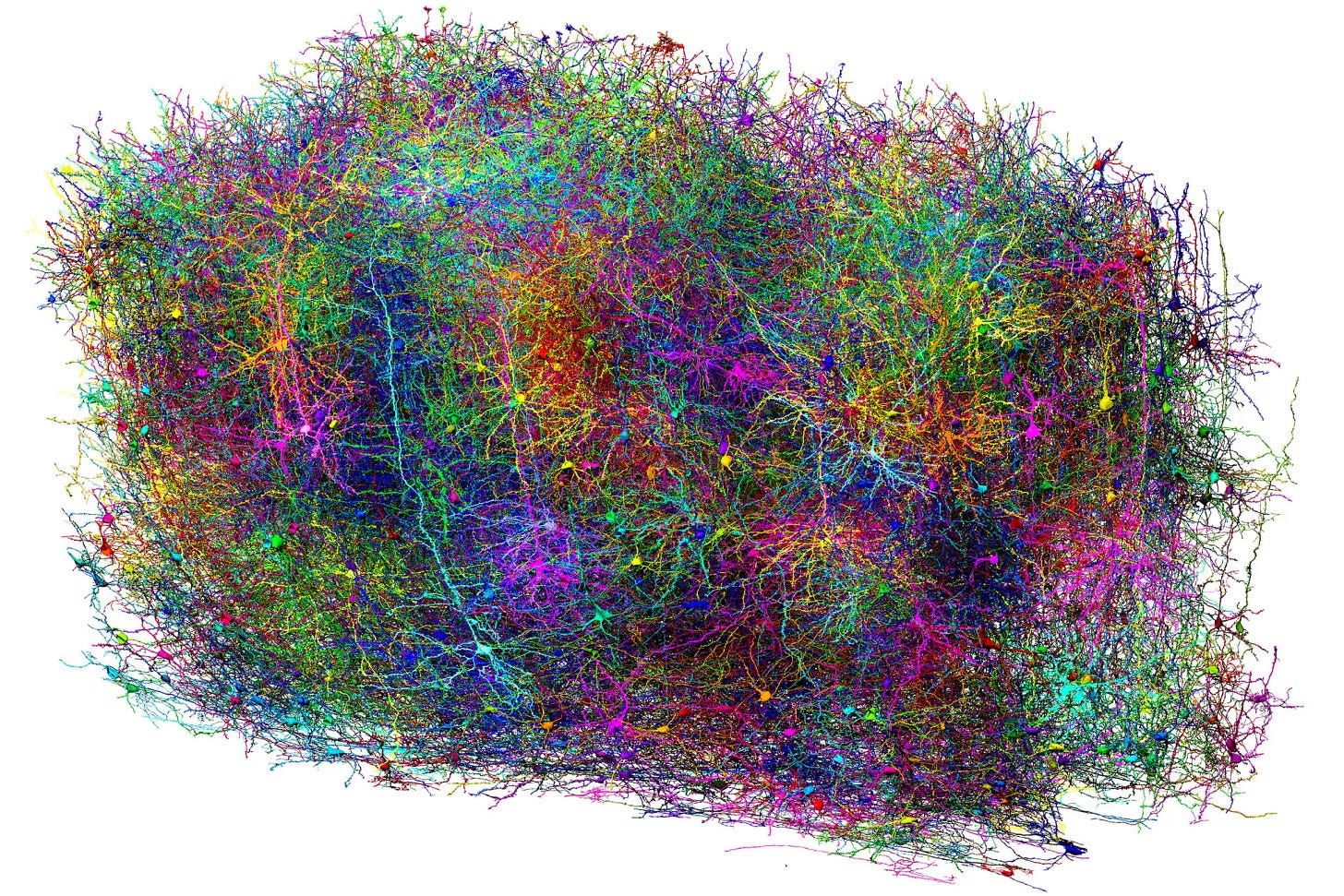

The target region, involved in visual processing, revealed previously undocumented wiring rules for specific inhibitory neurons like Martinotti and chandelier cells. This activity-linked dataset, published in Nature on April 9, 2025, offers a detailed blueprint for exploring how neural circuits relate to perception, computation, and disease.
Though the current dataset represents less than 1% of a mouse brain, researchers are now working toward full-brain mapping. Scaling efforts will depend on continued support from initiatives like the U.S. BRAIN Initiative, which faces funding pressure.
The dataset will be open to the neuroscience community, offering a foundation for future studies in precision neurotherapeutics and circuit-level intervention strategies.
Moving Away from Animal Testing
On April 10, 2025, the FDA announced a major shift in its regulatory approach, aiming to reduce—and eventually replace—animal testing requirements for monoclonal antibodies and other drugs. The agency will prioritize New Approach Methods (NAMs), including AI-driven toxicity models, lab-grown human organoids, and organ-on-chip systems.
Initial changes will focus on Investigational New Drug (IND) applications, where companies are now encouraged to include non-animal safety data generated through NAMs. Applicants may also incorporate verified international real-world safety data from regions with comparable regulatory standards. Submissions that demonstrate robust evidence from validated alternatives—such as AI-based models or human tissue systems—may qualify for streamlined regulatory review.
AI-driven platforms are being developed to simulate absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) profiles, as well as predict organ-specific toxicities by analyzing molecular structure and compound behavior in silico. These models offer early insight into potential safety concerns before any clinical or in vivo testing begins.
At the same time, human-derived organoids and organ-on-chip systems offer dynamic environments that replicate tissue-specific responses, revealing toxicity mechanisms that animal studies may miss—particularly those involving human-specific pathways or immune interactions.
FDA Commissioner Martin A. Makary called the transition a “paradigm shift,” implying faster patient access, stronger human relevance, and reduced use of animals—including dogs and primates. The agency is coordinating with NIH, the VA, and ICCVAM, with a pilot program launching soon to assess these methods in monoclonal antibody development.
A regulatory roadmap and public workshop are planned to guide the shift and gather stakeholder input.